French markets are bracing for significant volatility following President Emmanuel Macron’s announcement to dissolve parliament and call for fresh elections. This extraordinary move follows a strong performance by the far-right Rassemblement National (RN) in recent European elections, raising concerns about the country’s economic future.
Historical Context and Future Outlook
The far-right RN party’s proposal to reduce the retirement age to 60, akin to the notion of leaving the euro, was not well received by investors.
Historical precedents such as the Greek debt crisis, Brexit, and the Scottish independence referendum offer insights into how markets might react to significant political shifts like what is happening in France. Investors are likely to remain cautious, closely monitoring the election outcomes and subsequent policy announcements.
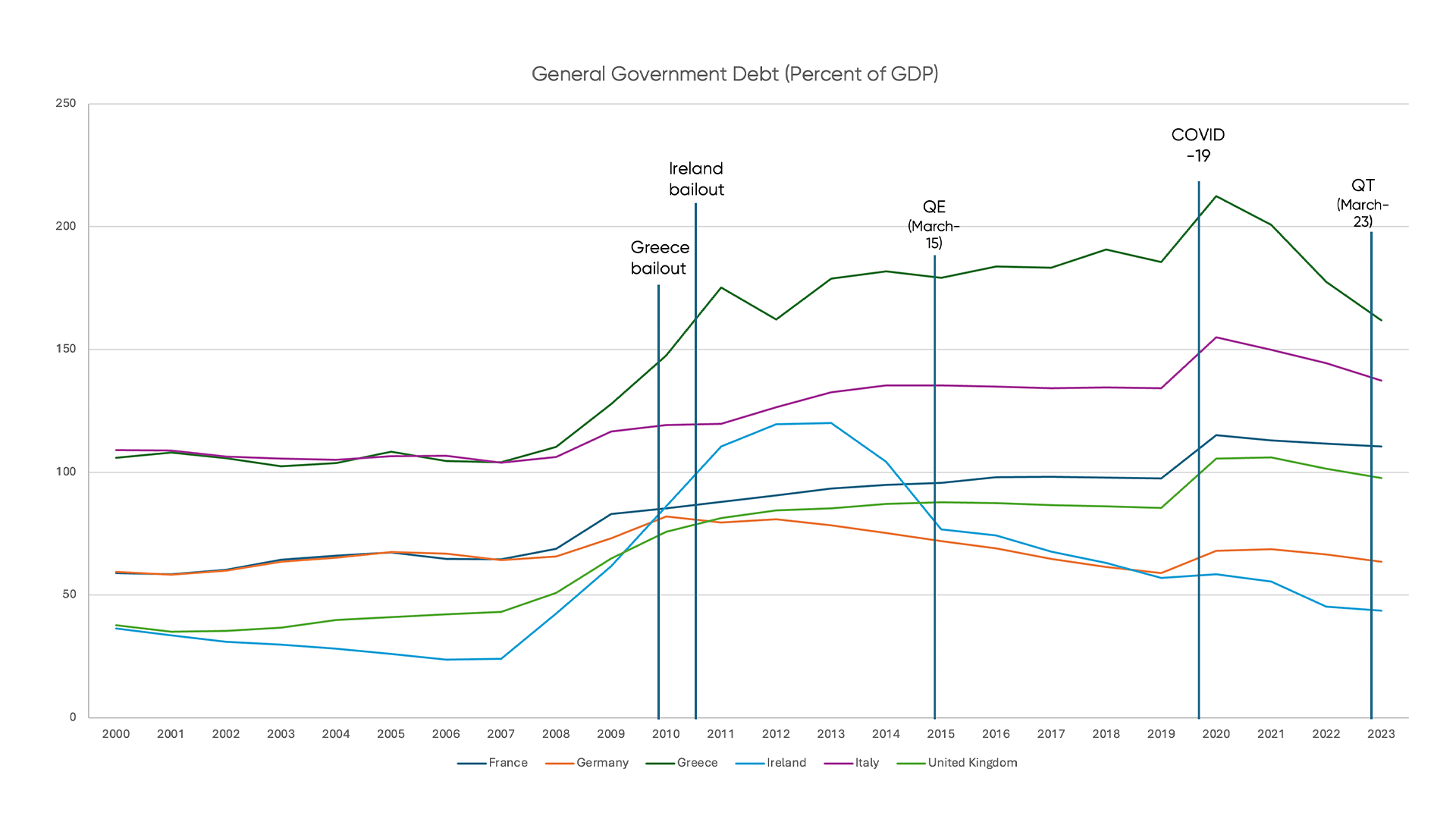
Following the 2007–2008 financial crisis, Greece faced a sovereign debt crisis known as “The Crisis.” In 2009, its debt-to-GDP ratio was 127.8%. According to Trading Economics, in 2023, France’s debt-to-GDP ratio was 111.6%.
Historical Debt Comparison France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy and the UK:
Figure 1: Historical General Government Debt Comparisons (Percentage of GDP).
Source: IMF and Trading Economics.
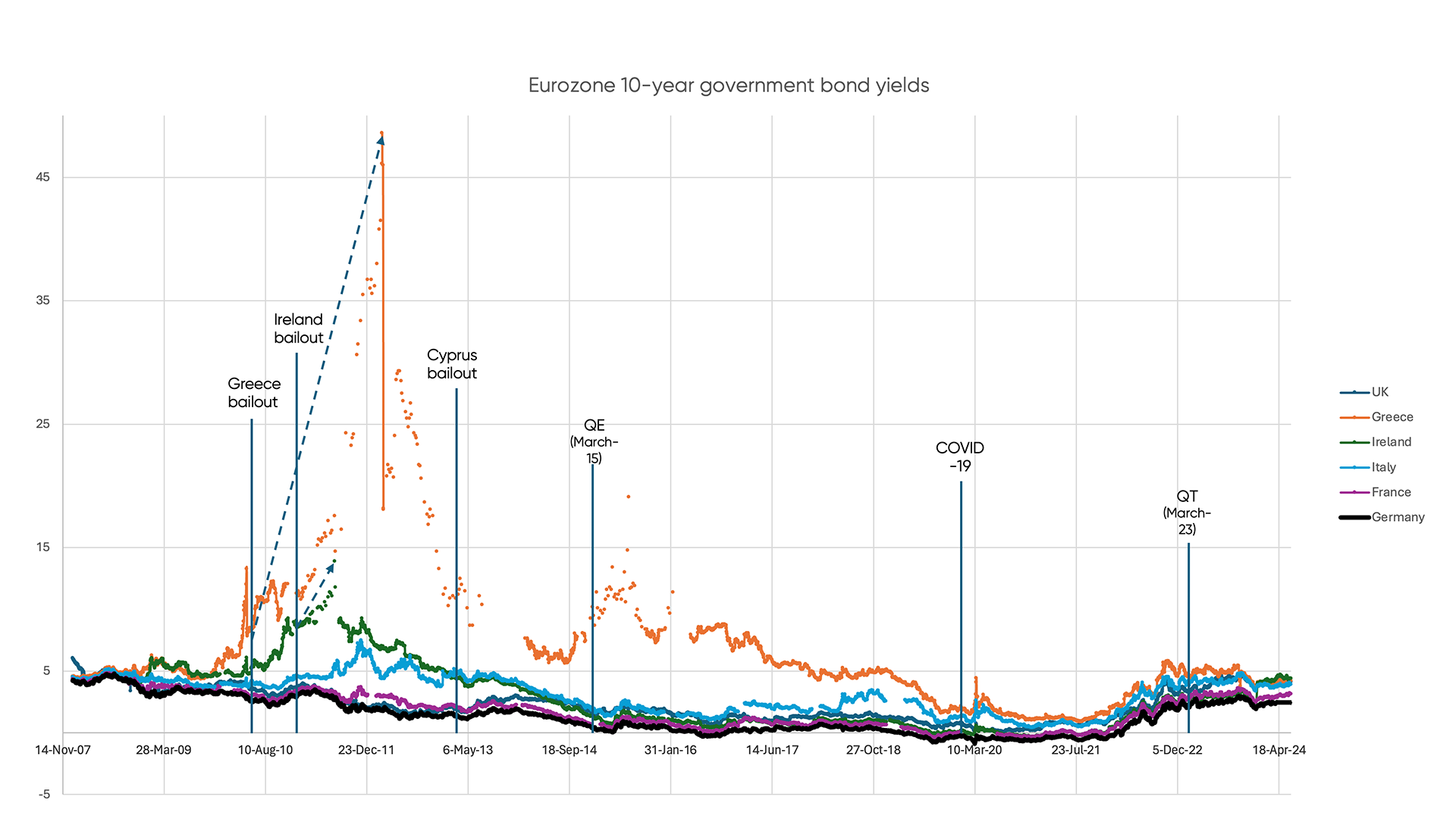
When a yield exceeds certain percentage points above the lowest comparable yield, usually the German Treasury Yield Curve among eurozone states, it signals significant concerns about the state’s creditworthiness.
Historical 10-year Government Bond Comparison:
Figure 2: Historical 10-Year Government Bond Comparisons.
Source: Confluence
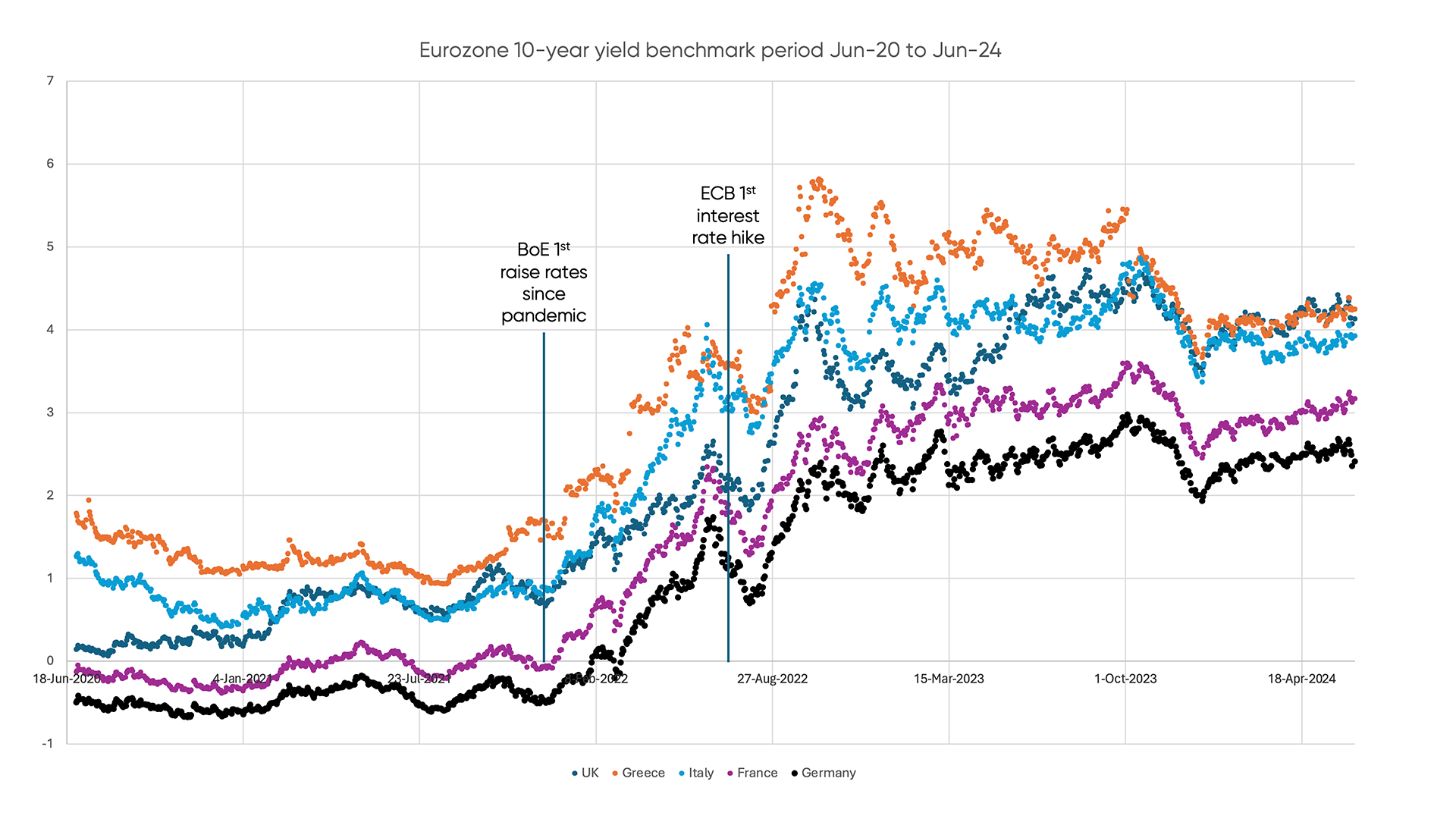
Due to rising global inflation, the BoE was the first big central bank to raise rates in December 2021 since the pandemic began. This also put more pressure on the ECB to tighten its policy, as the euro area had higher inflation and lower growth than the UK. However, the ECB faced a dilemma: higher rates could hurt the debt situation of some of its countries, like France, Italy, and Spain, which already had high interest rates and low growth prospects.
The BoE vs. ECB: 10-Year Bond Rates 20-24 Comparison:
Figure 3: 10-Year Government Bond Comparisons.
Source: Confluence
Upcoming Elections: Key Dates and Implications
The first round of the snap elections is set for June 30, with the decisive second round scheduled for July 7. The outcome could have profound implications for France’s political and economic stability. Given the RN’s recent gains and the lack of a clear majority in the National Assembly, Macron’s decision is seen as a high-stakes gamble. This situation leaves France with a fragmented political landscape, making it challenging for Macron to pursue his legislative agenda without forming new alliances or coalitions.
Market Reactions and Economic Concerns
French debt and equity markets have already felt the impact of the political uncertainty. The announcement has triggered a sell-off in French government bonds, pushing borrowing costs for some maturities above those of historically more volatile countries like Portugal. The yield on benchmark 10-year French bonds rose sharply, reflecting investor concerns over fiscal sustainability and economic policy direction under a potential RN-led government.
Often seen as the Eurozone’s benchmark for financial stability, the German bond yield is compared with the French bond yield in the chart below. This rapidly widening spread may be signally worsening fiscal conditions or investor confidence demanding higher returns for holding French debt. The gap between the 10-year French and German yields reached 79 basis points, marking the highest level since the European Sovereign Debt Crisis.
Spread Between 10-year French and German Bond yields:
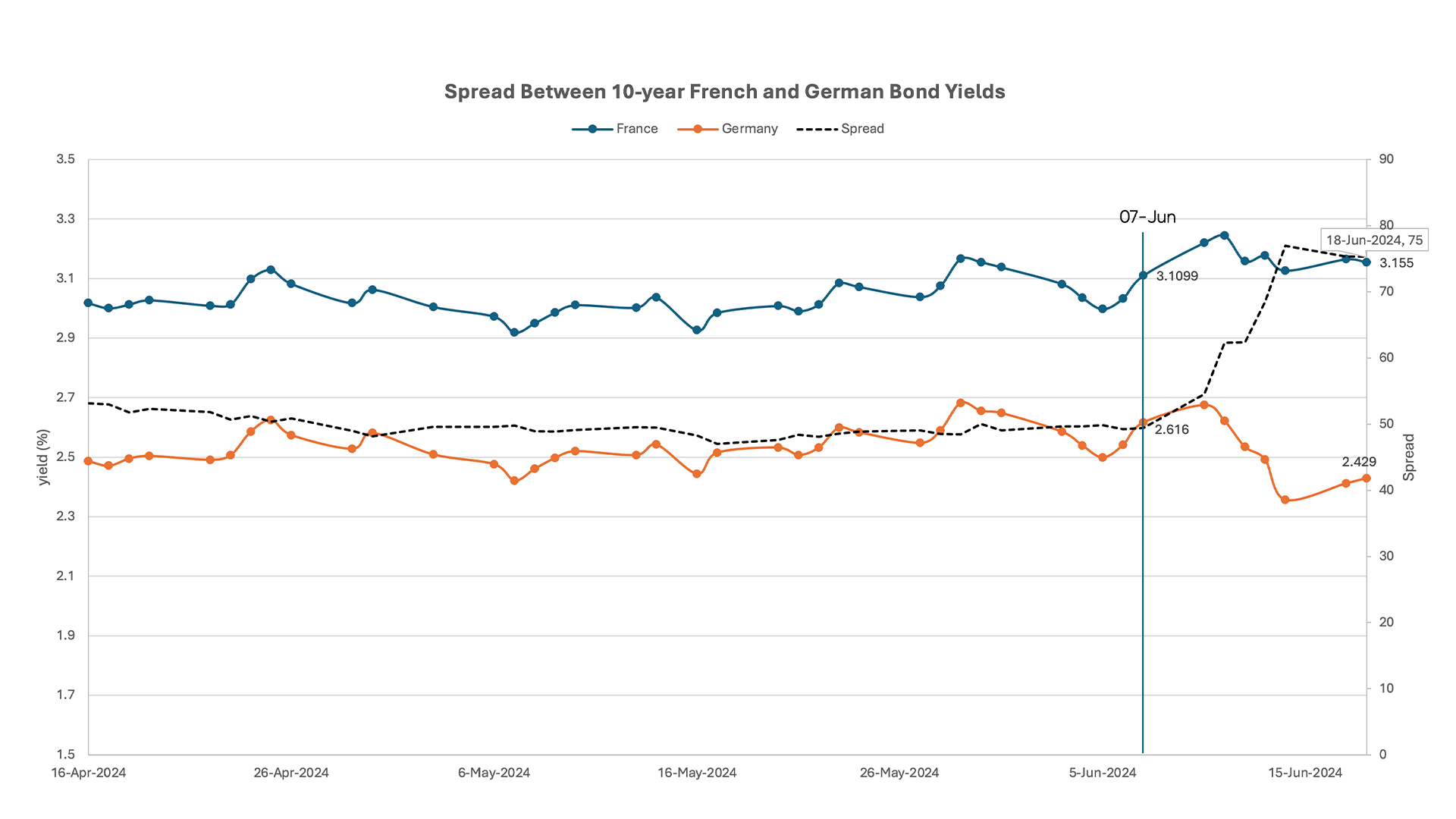
Figure 4: 10-year French and German Bond yields with Spread.
Source: Confluence
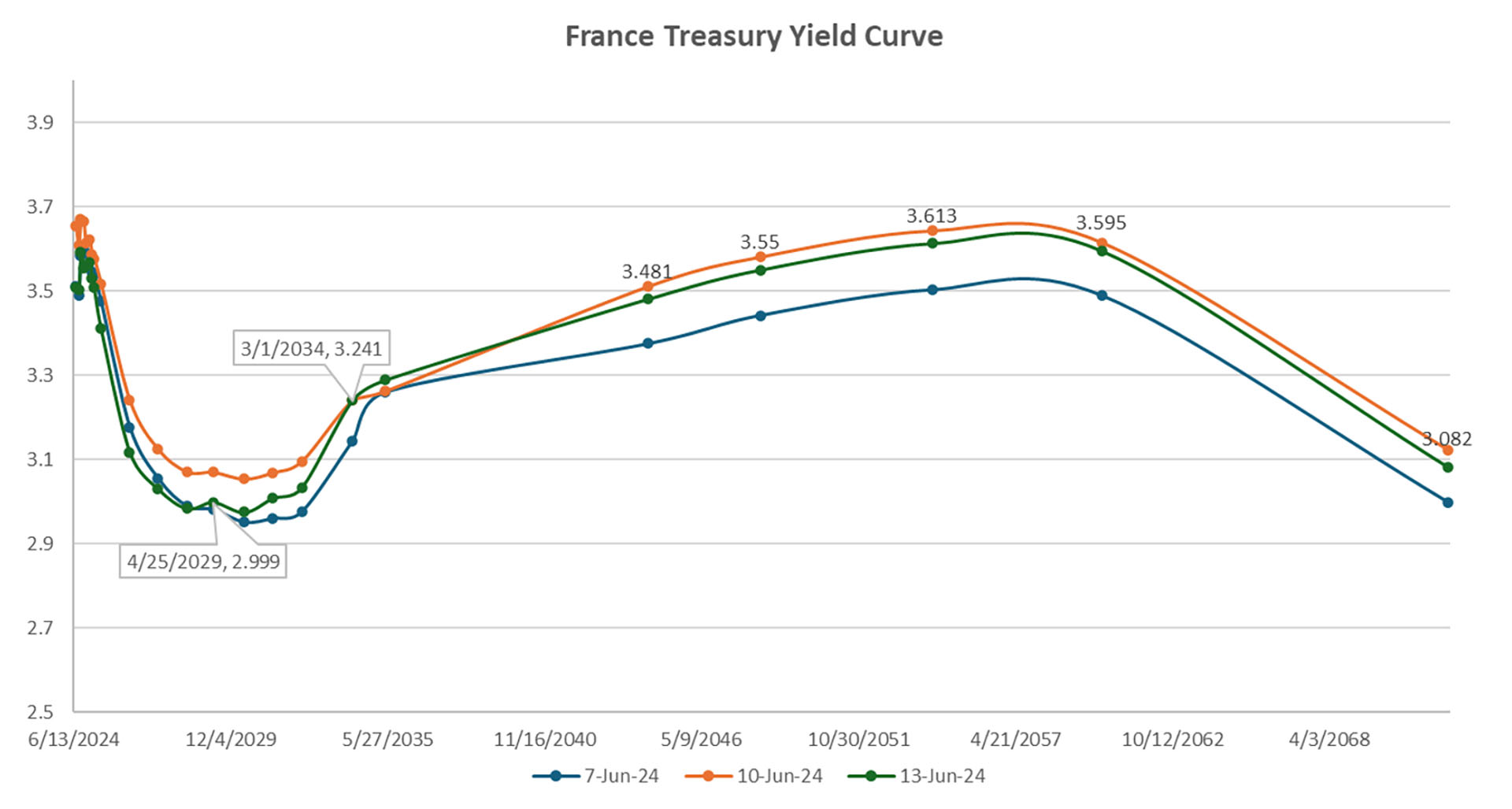
The snap elections announcement in France triggered a sharp increase in yield rates across the different tenors in the treasury yield curve. The 30-year yield bond climbed from 0.83% to 1.057%, indicating higher long-term borrowing costs for the French government.
French Treasury Yield Curve:
Figure 5: French Treasury Yield Curve. Highlighted rates correspond to the yields of Jun 13th, 2024.
Source: Confluence
Bruno Le Maire, France’s finance minister, has warned that the country could face a debt crisis like the UK’s gilt market turmoil during Liz Truss’s brief tenure as prime minister.
France’s fiscal sustainability and credit rating may be impacted by comparisons with other major economies, like the United States. Both nations have high public debt relative to GDP. However, differences between the two countries affect the manageability of their debt situations. The United States has a significant advantage over France in managing its debt because it issues debt in its own currency, the U.S. dollar, the global reserve currency. This status allows the U.S. to secure lower interest rates, eliminating currency exchange risk. The US can also use monetary policy to regulate debt and stimulate growth. In contrast, France, bound by the euro and ECB rules, has limited fiscal flexibility. Additionally, the US’s dynamic economy, with higher growth potential and a strong consumer market, better absorbs economic shocks. In contrast, France’s more rigid economy and smaller market make it more vulnerable to external fluctuations.
The 10-year US yield reached 4.20% on Friday, the 14th, partly influenced by signs of capital shifting away from French bonds. US yields have also shown high volatility, with intraday fluctuations as high as 20 basis points, indicating the market’s uncertainty and responsiveness to any information or cues from the Federal Reserve.
10-year US bond yield:
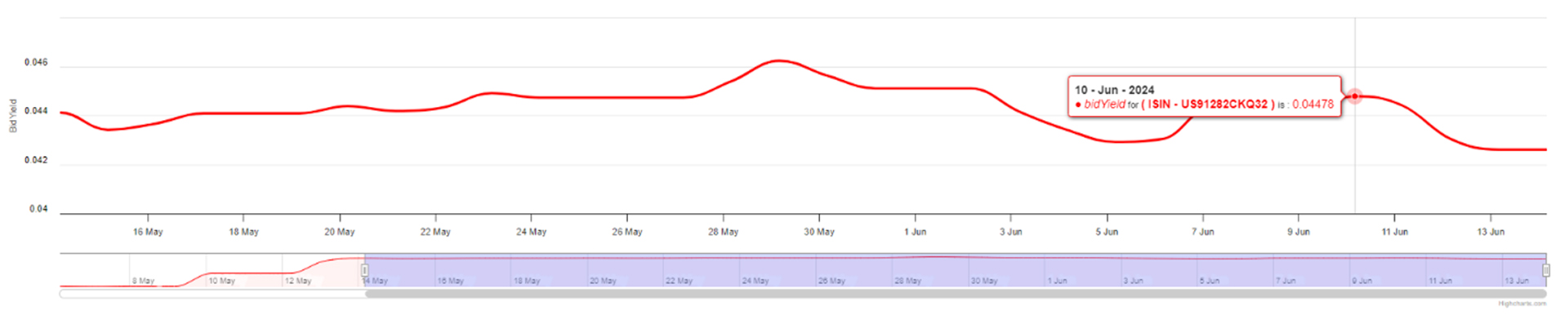
Figure 6: 10-year US bond yield.
Source: Confluence
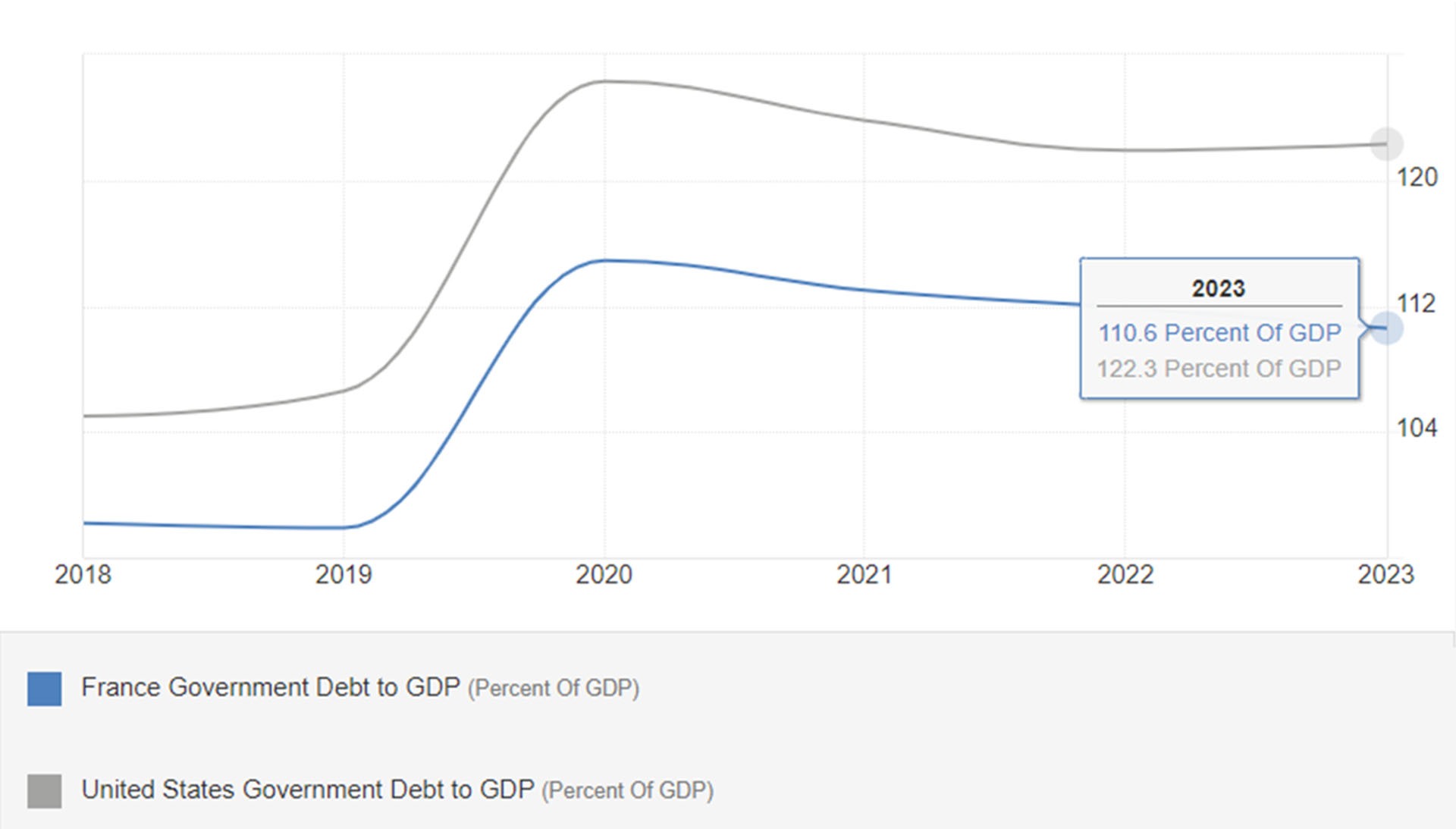
The chart below illustrates the diverging trends of the two countries. France’s debt ratio rose from 85.3% in 2010 to 110.6% in 2023, while the US’s debt ratio increased from 91.4% in 2010 to 122.3% in 2023.
France US Comparison Government Debt to GDP:
Figure 7: France US Comparison Government Debt to GDP.
Source: Trading Economics.
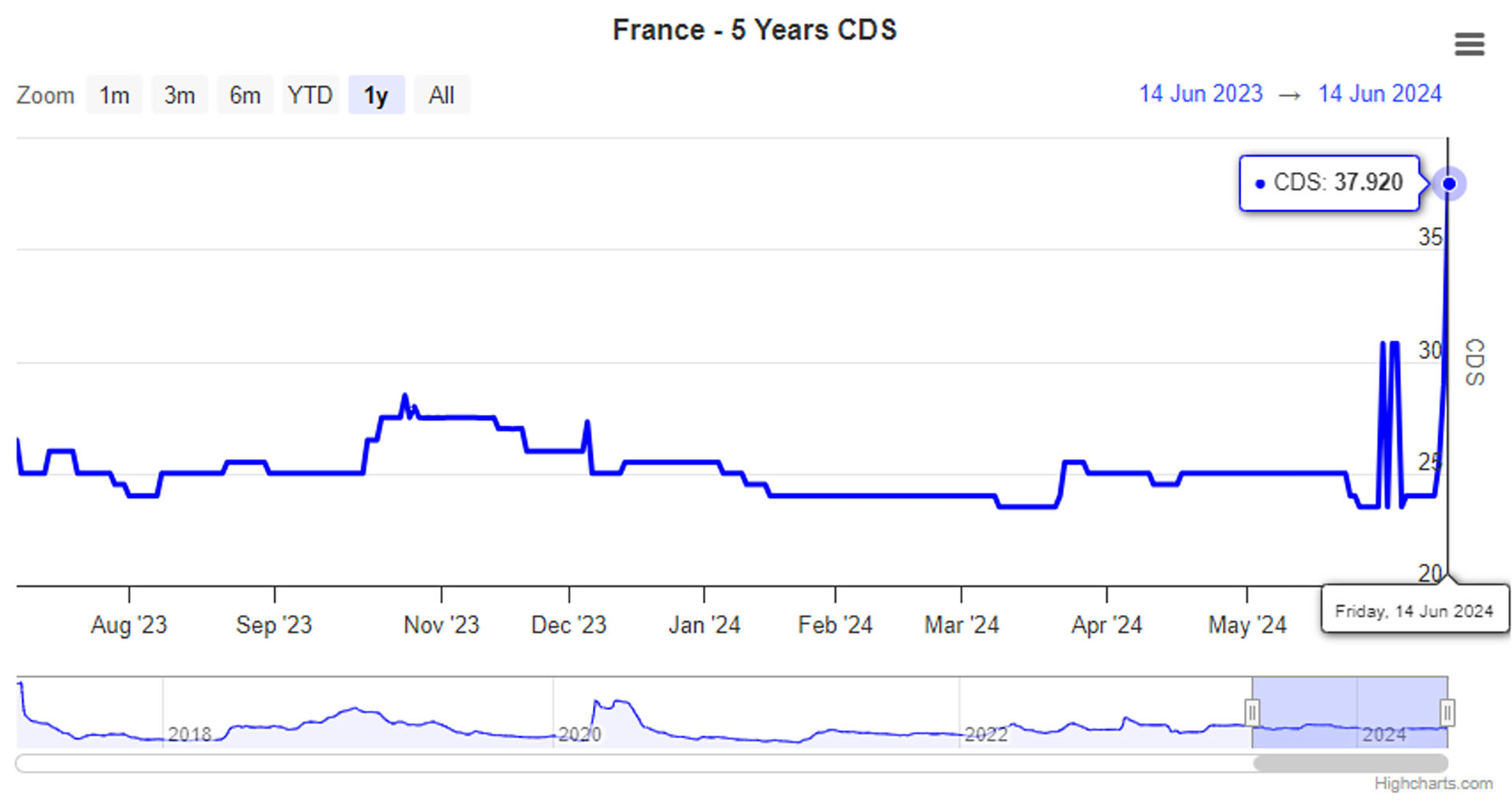
On June 18th, the France 5-Year Credit Default Swap (CDS) rose to 38.44 basis points, marking its highest level since May 2020. This metric is a crucial indicator used by investors to gauge the credit risk associated with French sovereign debt.
France 5-Year Credit Default Swap (CDS):
Figure 8: France 5 Years CDS.
Source: worldgovernmentbonds.com
Le Maire stressed that France cannot afford the economic policies of RN leader Marine Le Pen, which involve big increases in public spending, such as the idea of letting people retire at 60. According to The 2023 France Pension Reform by Intereconomics, France has the third highest total pension spending among OECD countries, after Greece and Italy, at around 14% of GDP. The OECD average is just above 9%. The pay-as-you-go (PAYGO) system covering private sector workers has become unsustainable, thanks to an aging population due to longer life expectancy (up 12 years since the 1960s), additionally the number of current contributors for one pensioner in France has shrunk from 4 in the 1960s to just 1.7.
Interconnected Risks in European Markets
French markets are closely correlated with those of other heavily indebted European nations, such as Italy. The financial system’s interconnectedness means that instability in French bonds could have broader repercussions across the Eurozone. Local banks, which are significant holders of government bonds, are particularly vulnerable to increased volatility and uncertainty.
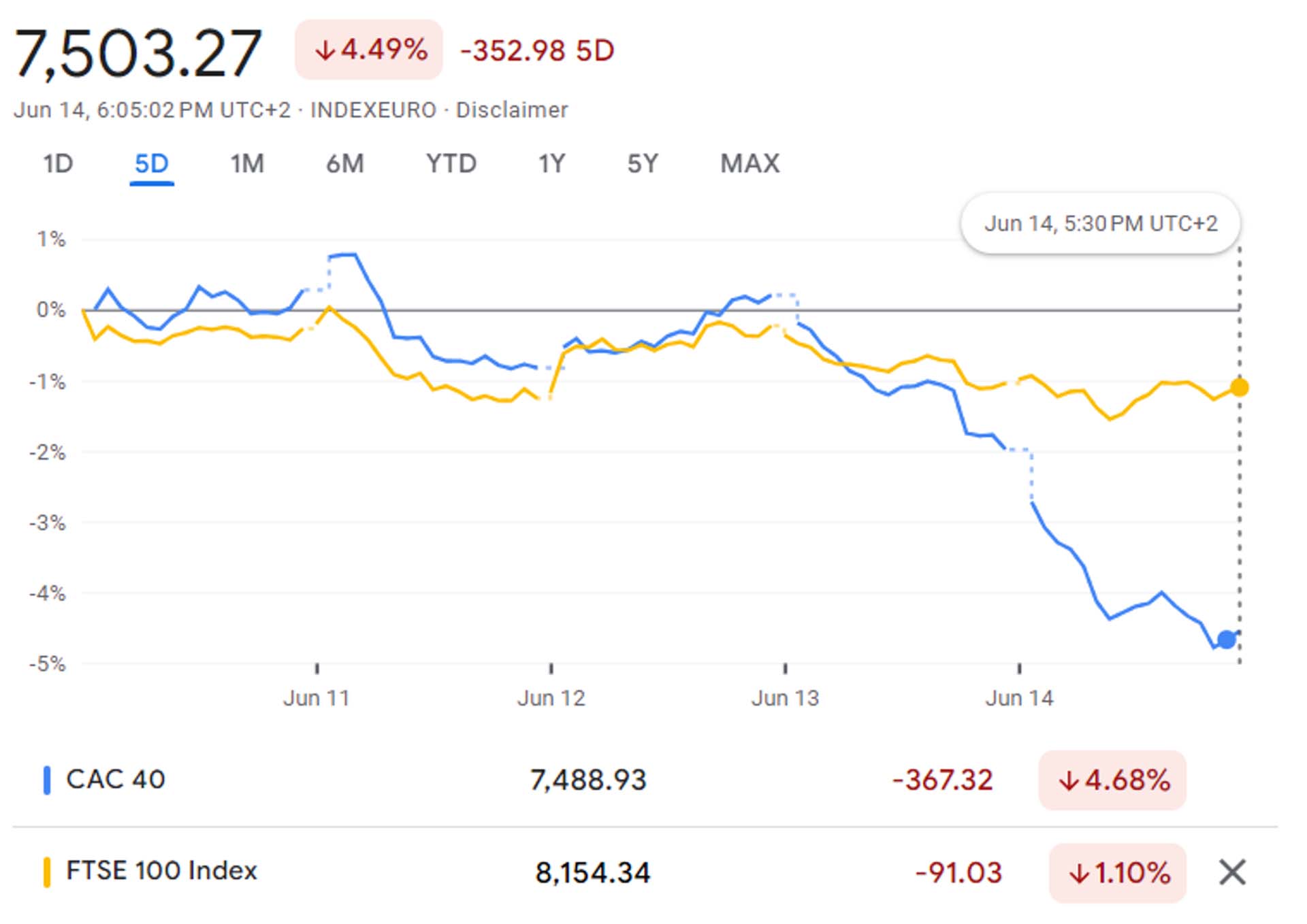
Performance of the French CAC 40 index against FTSE 100 since the snap election announcement:
Figure 9: CAC 40 and FTSE 100 comparison.
Source: Google Finance
President Emmanuel Macron’s surprise call for a snap election triggered a massive sell-off in the French stock market, wiping out $100bn, erasing all gains for 2024, and plunging the CAC 40 Index to its lowest level since March 2022. The index’s market capitalization dropped by about the size of Greece’s economy in one week as investors fled from the uncertainty and volatility of the political situation. The French election could have significant implications for the country’s fiscal and economic policies and its relations with the EU and the US, which could affect its growth prospects, debt dynamics, and borrowing costs.
Potential Scenarios and Investor Sentiment
The first round of elections will provide some indication of the political landscape, but the final outcome on July 7 remains uncertain. Market analysts expect continued volatility, with significant analysis required to understand the long-term impacts on financial markets. A strong showing by the RN could force Macron to appoint a far-right prime minister, introducing untested economic policies that might further unsettle markets.
As France navigates this period of political uncertainty, market participants must stay informed and agile. The upcoming elections hold significant implications for the country’s economic policy and financial stability. Investors are advised to closely monitor developments and prepare for a range of outcomes that could influence both the French and broader European markets.
Evaluated bond pricing in turbulent markets
Bond valuation is a complex and dynamic process that requires accurate and timely data, especially in volatile and uncertain market conditions. Confluence’s bond valuation platform provides firms with reliable and consistent bond valuations. The valuation methodologies are based on external inputs and adjusted according to spreads and other market factors. Trust Confluence’s bond valuations and valuation methodology to reflect your bond portfolio’s true value and help you make informed investment decisions in any market scenario.
The information contained in this communication is for informational purposes only. Confluence is not providing legal, financial, accounting, compliance or other similar services or advice through this communication. Recipients of this communication are responsible for understanding the regulatory and legal requirements applicable to their business.
Confluence is a leading global technology solutions provider committed to helping the investment management industry solve complex data challenges across the front, middle, and back offices. From data-driven portfolio analytics to compliance and regulatory solutions, including investment insights and research, Confluence invests in the latest technology to meet the evolving needs of asset managers, asset owners, asset servicers, and asset allocators to provide best-of-breed solutions that deliver maximum scalability, speed, and flexibility, while reducing risk and increasing efficiency. Headquartered in Pittsburgh, PA, with 750+ employees in 15 offices across the United Kingdom, Europe, North America, South Africa, and Australia, Confluence services over 1000 clients in more than 40 countries. For more information, visit:
www.confluence.com